- Diabetic Retinopathy
Human eye is like a camera in which retina acts as a film. Retina forms an ocular image, and then it is sent to brain via optic nerve. So any diseases of retina or optic nerve cause vision problem.
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of visual blindness if not diagnosed and treated early.
It is caused by changes in blood vessels in retina in which sometimes blood vessels may swell and release fluid or sometimes abnormal new vessels (neovascularisation) are formed.
Patients at risk are-
- Diabetes for longer duration
- Uncontrolled and fluctuating blood sugar levels (Check with HbA1C levels)
- Diabetes associated with Hypertension, deranged Lipid profile, anemia, pregnancy
Symptoms-
In early stages there are no signs and symptoms of diabetic retinopathy.
In advanced stages following symptoms may be seen
- Blurring of vision (can be gradual due to macular edema or sudden due to vitreous hemorrhage)
- Difficulty in reading and driving even with glasses
- Shadows or black spots/ floaters
How to diagnose Diabetic Retinopathy-
Every diabetic patient have at least once a year thorough eye checks up with dilated fundus check up as soon as Diabetes is detected. If there are any changes in retina then every 6 month dilated fundus evaluation is must.
We follow following protocol in our patients
- Visual acuity test
- Color vision test
- Dilated fundus evaluation to see any changes in retina e.g. hemorrhages or exuldates or abnormal new vessels(IRMA or neovascularisation) or macular edema
- Fundus Fluorescein angiography
- OCT macula test
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
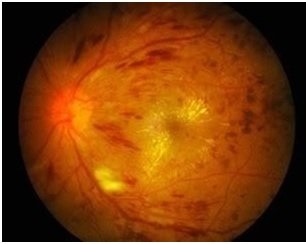
- Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy
- Proliferative Diabetic retinopathy
- Diabetic macular edema
Treatment options-
- Strict control of blood sugar, blood pressure or cholesterol levels
- If cystoids macular edema is diagnosed- macular grid photocoagulation is advised depending on macular thickness. Sometimes if macular thickness is more intravitreal injections are given first then macular photocoagulation
- In proliferative diabetic retinopathy- LASER PRP (pan retinal photocoagulation) around 1000-2000 laser burns are placed on retina away from macula which will shrink abnormal new blood vessels. In this two or more blood vessels are required. Sometimes post LASER some blurring of vision may be noticed by patient.
- If abnormal blood vessels are associated with bleeding- initially intravireal injections are given to stop bleeding. In no resolving and recurrent vitreous hemorrhage vitrectomy surgery may be required.
So in every known case of Diabetes mellitus dilated fundus examination is must every 6 months.
- Age related Macular degeneration (ARMD)
ARMD is age related changes in retina, usually affect after 50 years of age.
Patients complain of blurring of vision or distortion of images or black spot in the central vision.
Risk factors of ARMD-
- Family history of ARMD
- Smoking
- Alcohol consumption
- High Blood pressure, deranged lipid profile
- Poor diet low in fruits and vegetables
- UV light exposure- can cause damage to macular cells
Types-
- DRY ARMD-
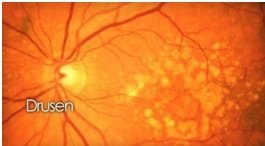
It develops slowly over many years and usually diagnosed during routine dilated retina examination. In some patients combinations of vitamins and antioxidants may reduce progression of DRY ARMD
Around 10-15% patients of DRY ARMD develop WET ARMD. So every diagnosed patients of Dry ARMD must have yearly dilated fundus examination
- WET ARMD-
It develops when abnormal blood vessels grow in macula which leak blood or fluid which later on leads to scarring of the macula. Patient complains of rapid loss of vision, distorted images, difficulty in reading books, sometimes central black spots in vision.
Distortion of images can be checked at home with Amsler grid test or patients are asked to check with grills of window.
Clinical diagnosis is confirmed with the OCT test and FFA test at hospital
Once confirmed- patient needs repeated once a month intravitreal injections for at least 3 months.
These injections help to stabilize the vision of patients and in some patients vision may improve in some extent.
3. Retinal Vein Occlusion-
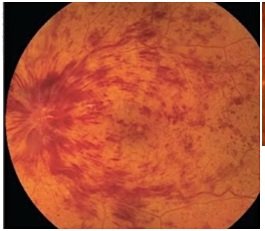
Retinal vein occlusion is a blockage of blood flow in any of retinal vein. It can occur in either a branch of retinal vein (Branch retinal vein occlusion- BRVO) or in the central retinal vein (Central retinal vein Occlusion- CRVO)
RVO causes bleeding in either in one quadrant of retina (BRVO) or in all quadrant of retina (CRVO) and macular edema.
Risk factors-
- Diabetes mellitus
- Hypertension
- Hyperlipidemia
- Heart disease
- Glaucoma
- Vasulitis
- Hypercoaguability
Treatment-
Intravitreal injections (Anti-VEGF) for macular edema and neovascularisation
LASER photocoagulation (PRP) – for macular edema in BRVO and neovascularisation in BRVO and CRVO - Retinal detachment
Retinal Detachment is separation of nine layers of neurosensory retina from underlying retinal pigment epithelium, which causes profound visual loss
Most retinal detachments are caused by one or more retinal holes or tears. Normal retina can develop holes due to ageing. If retinal detachmentment not treated early, there is a greater chance of permanent vision loss in the affected eye.
Types- - Rhegmatogenous RD
- Exudative RD
- Tractional RD
Normally vitreous is attached to the retina at several places. As the vitreous shrinks i.e as posterior vitreous detaches, it causes tear or hole in retina and liquefied vitreous passes through hole and detaches retina from its normal position.
Posterior vitreous detachment is normal ageing process; however it can occur at an earlier age in
• High myopic peoples (High minus spectacle number)
• History of cataract surgery
• Any ocular trauma
Tractional detachment is typically seen in people who have poorly controlled diabetes or other conditions.
In Exudative RD, fluid accumulates beneath the retina, but there are no holes or tears in the retina. Exudative detachment can be caused by age-related macular degeneration, injury to the eye, tumors or inflammatory disorders.
Warning signs-
Sudden appearance of floaters and flashes of light and sudden diminution of vision
Symptoms-
- Patients may notice floaters and of flashes of light
- Appearance of dark shadow in some part of side vision
- As the retinal detachment advances, and involves central retina, there is blurring of vision and significant diminution of vision
If any of above symptoms are noticed, consult urgently, as patient need dilated fundus examination with indirect ophthalmoscope.
Treatment of retinal detachment - Scleral buckling
- Vitrectomy
- Pneumatic retinopexy
Retinal detachment is an ophthalmic emergency, early to operate, better are the chances of visual recovery.
So Horizon Hospital always advice dilated fundus examination with indirect ophthalmoscope atleast once in a year.
Horizon Hospital has Best Retina Speciaslist In Pune
5 Macular Hole-
The macula provides the sharp, central vision that we need for reading, driving, and seeing fine details.
Macular hole is an opening in central part of retina (fovea) that leads to blurring, distortion or a grey spot in central vision.
Macular holes are related to aging and usually occur in people over age 60. Macular holes can also occur in other eye disorders, such as high myopia (nearsightedness), injury to the eye, retinal detachment, and, rarely, macular pucker.
Stages to a macular hole:
- Foveal detachments (Stage I). -Without treatment, about half of Stage I macular holes will progress.
- Partial-thickness holes (Stage II). -Without treatment, about 70 percent of Stage II macular holes will progress.
- Full-thickness holes (Stage III). – If left untreated, a macular hole can lead to a detached retina, a sight-threatening condition that should receive immediate medical attention
Symptoms-
- In early stages- slight distortion of images or blurring of vision
- Straight line or objects looks wavy
- Reading and performing other routine tasks with the affected eye become difficult.
Treatment-
Sometimes macular holes seal themselves and require no treatment
Surgical intervention- vitrectomy + air/gas tamponade
Vision improvement varies from patient to patient. Patients with macular hole for less than six months have better chances of visual recovery than those who have for a longer period.
6 Central Serous Retinopathy (CSR)
CSR is a condition which causes temporary or permanent impairment of vision. It usually affects men between 20 – 45 years of age and is associated with stress.
Symptoms-
Young male (usually) with type A personality can have
- sudden blurring /distortion of central vision
- loss of sensitivity in dim light
Treatment
Majority of the cases resolve on its own,
If swelling persists for more than 3-4 months – LASER treatment needed for persistent and recurrent cases.
7 Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)-
ROP is disorder of development of retinal blood vessels in premature babies.
Screening guidelines Indian scenario
• Infants with Birth weight <1700 gm • Gestational age of < 30 week • Exposed to oxygen >30 days
• Presence of other risk factor like respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, multiple blood transfusions, Twins/triplets, apnoeic episodes.
When should ROP baby examined?
Follow “Day-30 “strategy. Retinal examination of premature baby should be completed before day 30 of premature babies.
Treatment-
ROP can progress in 7-14 days, so needs a close follow-up.
ROP babies are treated with laser photocoagulation /intravitreal injections /surgery depending on the stage.
Horizon Hospital has Best Doctors For ROP
After treatment?
All ROP babies need regular eye examinations at least every 6 months as they are more prone for myopia..