
01.Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation is a well established and commonly performed procedure in cosmetic Surgery.
It is a surgical procedure to increase the size and shape of a woman’s breast.
It is commonly done by using a Silicone Implant which is placed under the existing Breast.
It is a simple day care surgery which gives gratifying results. To date there is no report in medical literature saying that placement of silicone implant increases the risk of cancer.
Indications-
- To improve the size and shape of the breasts for personal reasons, when a woman feels her breast size is too small.
- To correct sagging breasts after pregnancy & breastfeeding.
- To achieve symmetry if there is difference in breast size
- To reconstruct breast after removal of breast during cancer surgery.
Surgery
The surgery is performed in the operation theater in a strict sterile environment & requires hospitalization of one day.
It is done under General Anesthesia and usually done as a day care procedure.
A pocket is created under the Breast tissue by taking an incision in inframammary fold or the armpit. The implant is placed in this pocket either under the breast tissue(subglandular) or under the muscle over the chest wall(submuscular).
Implant placed in subglandular position gives better projection of nipple than submuscular position. Dressing is given to support the breast and hasten healing.
Recovery
Immediately after surgery the breast is supported with a dressing.
The patient can start moving around from the very next day.
Initial dressings will be removed over a period of several days and sports bra is advised.
Stitches do not require removal as they are absorbable. There may be some alteration in sensations over nipple and numbness may persist for few of weeks after surgery.
Breasts will probably be sensitive to direct stimulation for two to three weeks. Scars will be firm and pink for a minimum of six weeks. After few months, scars will begin to fade, although they will never disappear completely.
Regular examination by your plastic surgeon and routine investigations as prescribed will help assure that any complications, if they occur, can be detected early and treated.
Result
The result of Surgery is noticeable immediately.
The patient is advised to move the implant within breast tissue so as to form capsule of bigger size which reduces chances of capsular contracture. Your decision to undergo breast augmentation is a highly personal one that not everyone will understand. The important thing is how you feel about it.
If you set realistic goals, you will be happy with the outcome of the surgery.
Risk and Complications
Capsule contracture:
Formation of capsule around the implant is natural response of body.
The most common problem, capsular contracture, occurs if the scar or capsule around the implant begins to tighten.
This squeezing of the soft implant leads to a feeling of hardness on and around the breast. The incidence of capsular contracture has reduced with the advent of newer textured implants.
Though it is best prevented, Capsular contracture can be treated in several ways. It sometimes requires either removal or “scoring” of the scar tissue, or occasionally removal or replacement of the implant.
A few women can develop an infection around implant. This may occur at any time, but is most often seen within a week after surgery. Occasionally, the implant may need to removal for several months until the infection is cleared and new implant can then be inserted.
There is no evidence that breast implants cause breast cancer.

02. Breast Reduction
Women with disproportionately large & heavy breast may experience several health concerns like back and neck pain, breast pain and rashes under the breast apart from social and psychological embarrassment finding it uncomfortable to engage in physical activity or experiencing difficulty in finding clothes that fit.
The added weight of large breasts may exacerbate the symptoms for women with arthritis or spinal problems.
Breast reduction surgery removes excess fat, glandular tissue and skin to achieve a breast in proportion to the body. It will correct the functional symptoms as well as result in better proportioned breasts thereby enhancing a woman’s body image and self confidence.
The Best Candidates:
In most cases, breast reduction isn’t performed until a woman’s breasts are fully developed; however, it can be done earlier if large breasts are causing serious physical discomfort.
The best candidates are those who are mature enough to fully understand the procedure and have realistic expectations about the results.
Breast reduction is not recommended for women who intend to breast-feed in future.
Surgery:
Surgery involves reduction in size of the breast by removing excess fat, breast tissue and skin from the lower part of the breast;, shifting the nipple higher and reshaping and contouring of the breast.
The cuts are planned in the lower half of the breast and at the junction of the areola and skin.
These scars at the margins of the areola are usually not visible.
Other scars could be somewhat prominent, but fade over 1 to 2 years. (Poor healing and wider scars are more common in smokers.) There can be slight mismatch in breasts size or nipple position.
As surgery removes breast glandular tissue and many of the milk ducts leading to the nipples future breast-feeding may not be possible,
This procedure is done under general anesthesia. It takes 2 to 3 hours to reduce and reshape each breast. Hospital stay of 2 to 3 days is usually required.
Recovery:
After surgery, breasts are wrapped with an elastic bandage or a surgical bra over gauze dressings.
Placement of small tube in each breast may be needed to drain off blood and fluids for the first few days.
The dressings will be removed within two to three days after surgery, but surgical bra has to be worn 24×7 for several weeks, until the swelling and bruising subside. Stitches will be removed in one to three weeks.
Strenuous activities should be avoided for about 8 weeks after surgery. Routine activities are resumed after 1 week and light work can be resumed as early as 2 to 3 weeks.
Complications:
Like any surgical procedures there are potential risks and complications.
Some of risks include accumulation of blood (hematoma) or fluid (seroma),
Infection and poor healing and scar formation at the site of suturing.
Some specific risks include decrease in sensation at the nipple, decrease in blood supply at the nipple leading to partial or total necrosis of the nipple. This may need secondary reconstruction.
Risks are increased in smokers and diabetics.
The ability to breast feed after reduction is unpredictable and depends on the extent of reduction and type of technique used.
Result:
Most of the patients are very happy and satisfied with the results of breast reduction surgery.
Common question is. “Can the breasts become larger again? Occasionally, the breasts can become larger again, especially, if the patient gains excessive amounts of weight.
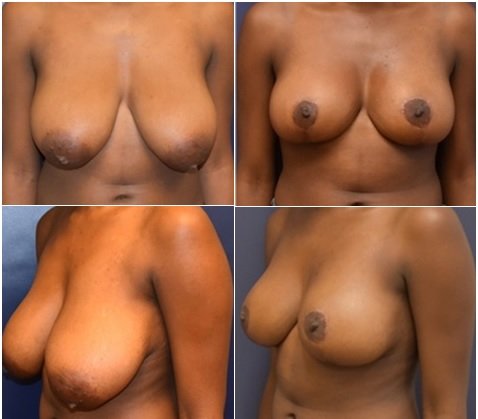
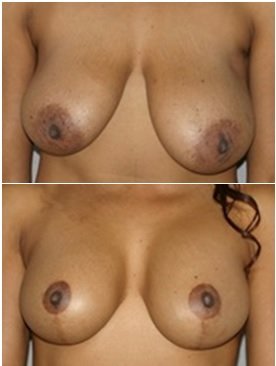
03. Mastopexy
Loss of skin elasticity with age, gravity and factors such as weight loss, physiological changes during pregnancy and breast-feeding ultimately affect the shape and firmness of breasts. Patients who are satisfied with the size, can undergo breast lift to raise and firm them, resulting in a more youthful breast contour. Some patients, who are unhappy breast volume and sagging, can benefit with breast lift along with implant augmentation to achieve desired result.
Procedure –
Breast lift is usually performed under a general anesthesia. One of the multiple techniques will be used, depending on the nature and degree of ptosis (sagging). Excess skin is removed by carefully chosen incisions around areola (the pigmented skin around the nipple) and sometimes on the breast below nipple and within the fold under the breast and the breast is reshaped to a more youthful appearance.
Recovery –
Pain and discomfort following surgery are not severe and can be controlled with oral pain medication. Stitches are removed within seven to ten days after surgery. Most patients can return to work within one week. It is recommended to wear a support bra for a few months after surgery. Bruising usually resolves in a week or two, some swelling may persist for four to six weeks or longer.
Limitations –
Don’t expect perfection.
Have realistic expectations. Know the risks associated with surgery.
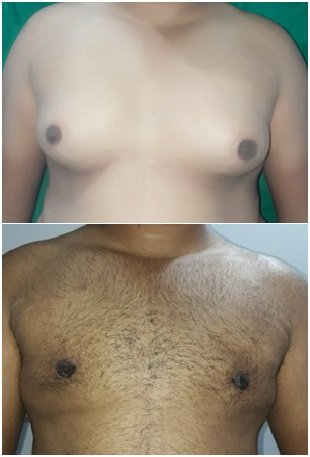
04. Gynecomastia
Normal breast tissue in male contains both fat tissue and glandular tissue (which is confined beneath nipple-areola complex and firmer than fat).
Removal of fat is lot easier than that of gland. Preoperative assessment of proportion of fat and glandular tissue is not always accurate.
Pseudogynecomastia – breast enlargement with more fat, normal gland
True gynecomastia – breast enlargement with excessive glandular breast tissue
Normal temporary gynecomastia occurs in babies (due to maternal estrogen) and in boys during puberty (relative estrogen excess) which regresses over time. Excessive fatty or glandular breast tissue causes untold embarrassment to young growing boys leading to psychological trauma necessitating timely treatment.
Surgery:
Liposuction with or without open gland excision through small periareolar incision is used to treat gynecomastia surgically.
Procedure is performed under general anesthesia.
All the excess fat and gland is removed. Incision is not sutured if drainage is needed.
Recovery –
Some swelling and bruising is expected and both will subside within few days to weeks.
A tight fitting surgical vest needs to be worn for 6 months to 1 year.
Risks and complications –
Apart from infection and hematoma, specific problems include alteration in sensation over Nipple and areola, loss of blood supply over skin of breast, surface irregularity etc.
05. Breast Reconstruction
Selective or total mastectomy results in breast asymmetry, scarring and noticeable volume reduction of the breast.
Breast reconstruction is a surgical procedure for women who have had partial or total removal of breast due to mastectomy or any other mishap to rebuild the mound of the breast to match the other breast.
Though breast conservation is becoming increasingly common, breast reconstruction is needed if a woman wants to improve her appearance post surgery.
Reconstruction can be planned with primary surgery (mastectomy) or later (secondary reconstruction).
Options
There are two major options for breast reconstruction surgery procedure:
- Silicone implants
- Tissue flap
These procedures use tissue from the woman’s back, thighs, tummy or buttocks to reconstruct the breast.
Depending on from where the tissue has been taken, it is termed TRAM flap (tissue taken from the abdomen), latissimus dorsi flap (tissue taken from back), gluteal free flap (tissue taken from the buttocks) or Inner thigh or TUG flap (uses tissue from the inner thigh)
While newer techniques are being developed for breast reconstruction surgeries, all the methods have their pros and cons. That is why it is important to consultant your plastic surgeon before choosing an option.
A few important Points before Breast Reconstruction Surgery
- The breast reconstruction surgery is a cosmetic surgery procedure, not a plastic surgery.
- A woman can choose to opt for mastectomy and a breast reconstruction procedure at the same time
- Implant breast reconstruction is almost always a two step procedure
- Depending upon which option you choose, the recovery period for breast reconstruction varies from one week to about eight weeks (two months)

06. Hypertrophic Axillary breast
Breast tissue makes up the shape and size of the breasts. However, it can sometimes develop beyond the normal location of the breasts. It is particularly common in the area of armpits (technically known as the axilla). According to medical studies, axillary breast tissue can occur in 2% to 6% of women.
Axillary breast tissue can make the area appear lumpy and “meaty”, especially with arms are down. It is thicker and more palpable. It may become particularly troubling before menstruating or with pregnancy, since the axillary breast can swell and feel more sensitive (just like breasts). Weight gain can make it look worse.
Axillary breast removal surgery
Axillary breast tissue can be safely removed with surgery. This can be done with liposuction if there is little correction required or exision (removing tissue with incisions) for extensive correction.
Benefits of surgery:
Elimination of undesirable contours in the underarm area
Improved mobility of the arms
Less irritation caused by clothing
Unique point: hidden scars
When more extensive correction is performed, the incisions are placed within the armpit fold. Scars will be well hidden by the natural crease. Sleeveless shirts can be without worrying about any scars being visible.
Procedure –
Local anesthesia is administered if liposuction is performed. General anesthesia is for surgery involving excision. Your procedure will take about an hour or so.
An incision is made within the armpit fold. This incision may measure just milimetres if liposuction is used. It may be a little longer if excision is performed. Through this incision, excess tissue is removed with the preferred technique. The incision is then closed and dressed.
Recovery
Restrictions on activity for a week or two
Some swelling, bruising and numbness for a few weeks
Results are visible in a couple of months
You’ll need to take about a week off from work for your initial recovery period.
Swelling can make the area look larger. As the swelling goes down, results of the surgery are evident.
Compression garment is recommended for a few weeks. Compression facilitate the retraction of skin for enhanced results.